How Do Related Tables Improve The Accuracy Of Data In A Database?
What is a relational database?
A relational database is a drove of information that organizes information points with defined relationships for easy admission. In the relational database model, the data structures -- including information tables, indexes and views -- remain separate from the physical storage structures, enabling database administrators to edit the concrete data storage without affecting the logical data structure.
In the enterprise, relational databases are used to organize data and identify relationships between fundamental information points. They make it easy to sort and find information, which helps organizations make business decisions more efficiently and minimize costs. They piece of work well with structured information.
How does a relational database work?
The data tables used in a relational database store information almost related objects. Each row holds a tape with a unique identifier -- known equally a key -- and each column contains the attributes of the data. Each record assigns a value to each feature, making relationships between data points easy to identify.
The standard user and application program interface (API) of a relational database is the Structured Query Language. SQL code statements are used both for interactive queries for information from a relational database and for gathering data for reports. Defined data integrity rules must be followed to ensure the relational database is accurate and accessible.
What is the structure of a relational database model?
E. F. Codd, then a young programmer at IBM, invented the relational database in 1970. In his paper, "A Relational Model of Data for Large Shared Data Banks," Codd proposed shifting from storing data in hierarchical or navigational structures to organizing data in tables containing rows and columns.
Each table, sometimes called a relation, in a relational database contains ane or more data categories in columns or attributes. Each row, too chosen a record or tuple, contains a unique case of information -- or key -- for the categories defined past the columns. Each table has a unique master primal that identifies the information in a table. The human relationship betwixt tables can exist set via the apply of foreign keys -- a field in a tabular array that links to the primary key of some other tabular array.
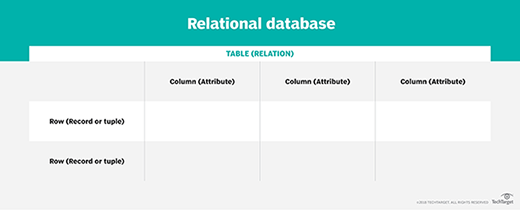
For example, a typical business order entry database would include a table that describes a client with columns for proper noun, address, phone number and so forth. Another table would describe an order, including information similar the production, customer, engagement and sales price.
A user tin get a database report showing the information they need. For instance, a co-operative office manager might want a report on all customers that bought products afterward a certain date. A financial services managing director in the same company could, from the same tables, obtain a report on accounts that demand to be paid.
When creating a relational database, users define the domain of possible values in a data column and constraints that may use to that data value. For case, a domain of possible customers could allow upwards to 10 possible customer names, but it is limited in ane table to assuasive merely three of these customer names to be specifiable.
Two constraints relate to data integrity and the chief and strange keys:
- Entity integrity ensures that the primary key in a tabular array is unique and the value is not set to null.
- Referential integrity requires that every value in a foreign key column will be found in the primary key of the table from which it originated.
In addition, relational databases possess physical data independence. This refers to a system's capacity to make changes to the inner schema without altering the external schemas or application programs. Inner schema alterations may include the following:
- the utilise of new storage devices;
- modifying indexes;
- irresolute from a specific admission method to a different one;
- using different data structures; and
- using diverse storage structures or file organizations.
Logical information independence is a system'due south ability to manage the conceptual schema without altering the external schema or awarding programs. Conceptual schema alterations may include the addition or deletion of new relationships, entities or attributes without altering existing external schemas or rewriting application programs.
What are the types of databases?
There are several database categories, from basic apartment files that aren't relational to NoSQL and newer graph databases that are considered even more relational than standard relational databases. Some database types include the following:
Apartment file database. These databases consist of a unmarried tabular array of data that has no interrelation -- typically text files. This type of file enables users to specify data attributes, such as columns and information types.
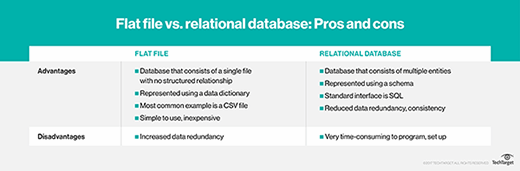
NoSQL database. This type of database is an culling that's peculiarly useful for large, distributed data sets. NoSQL databases back up a variety of data models, including cardinal-value, certificate, columnar and graph formats.
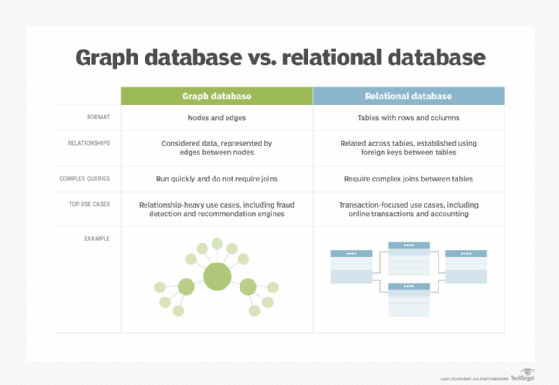
Graph database. Expanding beyond traditional cavalcade- and row-based relational data models; this NoSQL database uses nodes and edges that represent connections betwixt data relationships and can notice new relationships betwixt the data. Graph databases are more sophisticated than relational databases. They are used for fraud detection or spider web recommendation engines.
Object relational database (ORD). An ORD is composed of both a relational database management organization (RDBMS) and an object-oriented database management system (OODBMS). Information technology contains characteristics of both the RDBMS and OODBMS models. A traditional database is used to store the data. It is and so accessed and manipulated using queries written in a query language, such as SQL. Therefore, the bones approach of an ORD is based on a relational database.
Even so, an ORD can besides exist considered object storage, particularly for software written in the object-oriented programming language, thus pulling on object-oriented characteristics. In this situation, APIs are used in the storage and retrieval of data.
What are the advantages of relational databases?
The key advantages of relational databases include the following:
- Categorizing data. Database administrators tin easily categorize and store data in a relational database that tin can and then be queried and filtered to extract data for reports. Relational databases are too piece of cake to extend and aren't reliant on physical organization. After the original database creation, a new information category can be added without having to modify the existing applications.
- Accuracy . Information is stored just one time, eliminating data deduplication in storage procedures.
- Ease of use. Complex queries are easy for users to carry out with SQL, the master query linguistic communication used with relational databases.
- Collaboration. Multiple users can access the same database.
- Security. Direct access to information in tables within an RDBMS can be express to specific users.
What are the disadvantages of relational databases?
The disadvantages of relational databases include the following:
- Structure. Relational databases crave a lot of construction and a sure level of planning because columns must exist divers and data needs to fit correctly into somewhat rigid categories. The structure is expert in some situations, but it creates issues related to the other drawbacks, such as maintenance and lack of flexibility and scalability.
- Maintenance bug. Developers and other personnel responsible for the database must spend fourth dimension managing and optimizing the database every bit information gets added to it.
- Inflexibility. Relational databases are not ideal for handling large quantities of unstructured data. Information that is largely qualitative, not easily defined or dynamic is non optimal for relational databases, because every bit the data changes or evolves, the schema must evolve with it, which takes time.
- Lack of scalability . Relational databases do not horizontally scale well across physical storage structures with multiple servers. It is hard to handle relational databases across multiple servers considering as a data set gets larger and more distributed, the structure is disrupted, and the use of multiple servers has effects on operation -- such as application response times -- and availability.
Examples of relational databases
Standard relational databases enable users to manage predefined data relationships across multiple databases. Pop examples of standard relational databases include Microsoft SQL Server, Oracle Database, MySQL and IBM DB2.
Cloud-based relational databases, or database as a service, are also widely used because they enable companies to outsource database maintenance, patching and infrastructure support requirements. Cloud relational databases include Amazon Relational Database Service, Google Cloud SQL, IBM DB2 on Cloud, SQL Azure and Oracle Cloud.
What are the differences betwixt relational databases, non-relational databases and NoSQL?
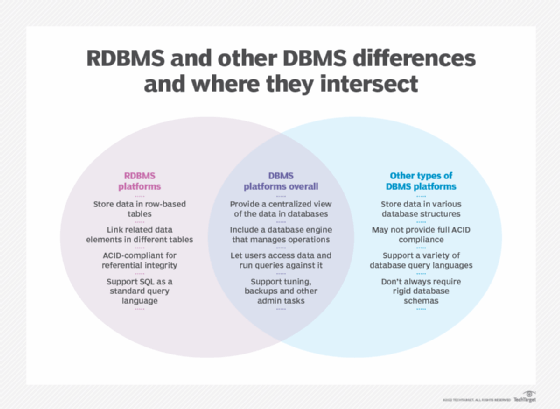
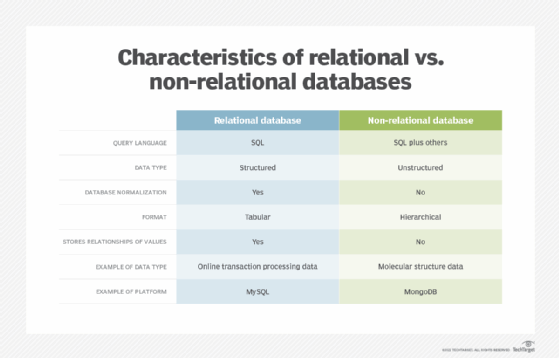
The most important difference between relational database systems and not-relational database systems is that relational databases are normalized. That is, they store data in a tabular grade, arranged in a tabular array with rows and columns. A non-relational database stores information equally files.
Other differences include the following:
- Use of master keys. Relational database tables each have a primary central identifier. In a non-relational database, data is usually stored in hierarchical or navigational form, without the use of primary keys.
- Information values relationships. Since data in a relational database is stored in tables, the relationship betwixt these data values is stored as well. Since a non-relational database stores data as files, there is no human relationship between the information values.
- Integrity constraints. In a relational database, the integrity constraints are whatever constraint that ensures database integrity. They are defined for the purpose of atomicity, consistency, isolation and durability, or ACID. Non-relational databases practise not use integrity constraints.
- Structured vs. unstructured information. Relational databases piece of work well for structured data that conforms to a predefined information model and doesn't change much. Non-relational databases are improve for unstructured data, which doesn't adjust to a predefined data model and can't be stored in an RDBMS. Examples of unstructured data include text, emails, photos, videos and web pages.
Non-relational databases are besides called NoSQL databases. The terms are used interchangeably, but there are differences.
SQL is the query language that is used with relational databases. Relational databases and their direction systems almost always use SQL every bit their underlying query linguistic communication. NoSQL, or not only SQL, databases employ SQL and other query languages. For example, the NoSQL database direction programme MongoDB uses JSON-similar documents to store and organize data. (Technically, it uses a variant of JSON telephone call BSON, or binary JSON.)
Referring to databases as non-relational vs. relational categorizes them based on their architecture, and referring to them every bit SQL vs. NoSQL categorizes them based on the query language, whether it is solely SQL or not only SQL. Often, a relational database can exist referred to equally a SQL database, equally many of them use SQL, and non-relational databases can be referred to as NoSQL databases. NoSQL and non-relational databases work well with more fluid data models, such as in engineering parts and molecular modeling, where the data is always changing.
Both relational and not-relational database platforms have their drawbacks. NewSQL databases seek to provide the benefits of both types, by offering the data integrity and awarding access control that relational databases offer and the horizontal scalability that non-relational or NoSQL platforms provide.
Choosing the correct database
Relational databases work for structured data with defined relationships that can exist organized in a tabular format. All the same, there is a lot more to selecting the right database compages than just choosing between relational and non-relational. The type of data and awarding existence used or developed are key factors to consider. Larn some of the other factors to consider when choosing a database model for an enterprise application.
Certain initiatives require specific considerations when choosing database software. For instance, with IoT initiatives, SQL vs. NoSQL is an event, equally is static vs. streaming. Find out what to appraise when selecting a database for an IoT project.
How Do Related Tables Improve The Accuracy Of Data In A Database?,
Source: https://www.techtarget.com/searchdatamanagement/definition/relational-database
Posted by: smithwiting.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How Do Related Tables Improve The Accuracy Of Data In A Database?"
Post a Comment